Conversation API
How to integrate own channels and custom interfaces in Syntphony CAI
What is the conversation API
Any developer can integrate their own channels to Syntphony CAI. A user could benefit from a chat in the company’s website using a custom interface or even custom templates for responses, such as graphs, masked inputs or interaction with other elements of the webpage.
Companies normally add chatbot platforms to their existing app, or use one of the internal channels to release a virtual agent for its employees. When using Syntphony CAI, this can be done by consuming the Conversation API described below.
Authentication
Authentication must be handled following the OAuth2 Bearer Token protocol, where one must authenticate with a valid, expirable token. Including the Bearer Token in your header is mandatory from the API version 4.x and onwards.
Once obtained, the access token must be sent in your header ‘Authorization’ as the string: “Bearer {{access_token}}”
Obtaining your Authentication Token
To generate a token, make a request on the following endpoint:
POST
{{keycloak_url}}/auth/realms/{{org_name}}/protocol/openid-connect/tokenIn distinction to the Integration API, the Conversation API authenticates with a pair of client credentials, persistent across all of your third party channels and services which might need a stable, consistent access.
Request Body
client_id: {{‘clientName’}}
client_secret: {{‘clientSecret’}}
grant_type: client_credentialsContent-Type is ‘x-www-form-urlencoded’. Client_id and client_secret are your provided client credentials for API usage; grant_type is a fixed value of 'client_credentials'.
Those credentials are delivered to you on environment creation, but should you lack said credentials, you may open a ticket requesting this information in this page.
Sample Response Body
While there are several, default fields that you may map from the OAuth2 response body, we recommend you to map those, as they are the only ones you will need to use.
Name
Type
Description
access_token
String
Your bearer token. Can be as long as 800 characters.
expires_in
Integer
Lifetime of your token, in seconds.
refresh_expires_in
Integer
Lifetime of your refresh token, in seconds.
refresh_token
String
Your refresh token, used to renew your token. (See below)
Sample response
Authentication Token Renewal
Authentication tokens may expire, as indicated by the ‘expires_in’ field from the token generation response. Slightly different from the user credentials renewal, though, you must still provide your client credentials. You may do this, by calling the same endpoint, but with the following request body:
Renewal Request Body
Once again, Content-Type is ‘x-www-form-urlencoded’. If your refresh_token has also expired (indicated by the field ‘refresh_expires_in’), you are required to generate a new token by reentering the client credentials.
Conversation services
The conversation service is where you implement your own Syntphony CAI web or custom channel. By using our methods, you can handle any conversation Syntphony CAI performs, besides being able to execute auxiliary methods, such as like and disliking replies and evaluation the conversation.
Input Type
When implementing the conversation API, you are able to handle both Text and Audio inputs. This means that this implementation allows you to use your Web, Web Mobile and Custom (Such as in proprietary apps through JSON implementation) channels with both text and audio inputs.
Both inputs use the same endpoints and their session codes are interchangeable, so your user may submit an input through audio and choose to type afterwards without breaking the conversation.
The body of the request will change when using Audio inputs, and this is detailed below.
(Text) Conversation Service HTTP API
Conversation service (Live)
Method
POST
URL:
/org/{orgUUID}/env/{envUUID}/bot/{botUUID}/channel/{channelUUID}/v1/conversations or /org/{orgUUID}/env/{envUUID}/bot/{botUUID}/channel/{channelUUID}/v1/conversations/{sessionCode}
Type:
application/json
The conversation service is used to execute a conversation from any given channel. Each call to this service is a message from a user that the virtual agent must process in order to understand and answer the user.
Authorization is required, organization specific and slightly configurable. The permissions from the user provided to request the token will be reflected on access, as specified on Authentication. Any calls will be refused whenever a token does not grant access to the provided Organization, Environment or Bot parameters, whenever it is revoked and whenever it expires.
This endpoint is interchangeable with it's Audio Input variant.// Some code
URL Parameters
By default, the session code will expire after 30 minutes. This value is set in eva-broker deployment settings. Contact your system administrator for details.
Name
Type
Required
Description
orgUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of your organization. Your token is verified over this field.
envUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of the environment your bot is located. Your token is verified over this field.
botUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of the bot your channel is located. Your token is verified over this field.
channelUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of the channel.
sessionCode
String
No
The current conversation's ID. Any first call to Syntphony CAI’s conversation service must have this parameter empty. After the first call, this parameter is required in order to give continuity to the conversation. It is returned in the service’s response.
Request headers
Name
Type
Required
Description
API-KEY
String
Yes
An API key for client identification. The environment administrator must provide this data.
OS
String
Yes
The user's operating system. Example: for web chat, it might be Windows; and for a mobile app, iOS.
OS-VERSION
String
No
The version of the operating system above.
BROWSER
String
No
User’s current browser, when using one.
BROWSER-VERSION
String
No
The version of the browser above
USER-REF
String
Yes
This field is used for identifying the user by a technical value, depending on the channel. Some examples:
- For web chat: the user IP address
- IVR: phone number
- Messenger: Facebook’s user ID
BUSINESS-KEY
String
No
This field is used to identify the user in a business level if the channel has information about the user. Examples:
- In a private section of a webpage that requires logging in, the business key might be the user login
- User document number
- Client #
LOCALE
String
Yes
The virtual agent’s language: <language>-<COUNTRY>
This must be the same as configured in the Cockpit.
Examples: en-US es-ES pt-BR
If you lack your API KEY, you may request it through a ticket here.
Request body
Name
Type
Required
Description
text
String
No, if 'code' was provided or this is an Audio Request. Otherwise, yes.
A text input by a user or a transcription from an audio. This value must be empty if 'code' was provided.
code
String
No, if 'text' was provided or this is an Audio Request. Otherwise, yes.
On the first call of a conversation, the code “%EVA_WELCOME_MSG” can be sent to execute a custom Welcome flow created in the Cockpit.
This code may also be used to locate a specific answer. Learn more here.
Either this value or a text This value must be empty if "text" was provided.
intent
String
No
This parameter is only used with Intent Navigator behavior (Intent Navigator). Name of the intent identified
confidence
Double
No
This parameter is only used with Intent Navigator behavior (Intent Navigator). Confidence score for the intent, from 0 to 1
entities
JSON Object
No
This parameter is only used with Intent Navigator behavior (Intent Navigator). Entities as Json object containing fields (string, string) with the different entities detected in as key (entity name) and value (entity value)
Advanced Options
Name
Type
Required
Description
Multilanguage
Name
Type
Required
Description
translateInput
Boolean
No
This parameter is used when we don't want to translate the user's input
Response body
Name
Type
Description
text
String
The same text sent in the request. No text is provided if 'code' was sent instead.
sessionCode
String
A conversation identifier, generated in the first request. This must be sent in the following calls in the URL as explained URL parameters in this chapter.
answers
Answer[]
A list of responses that may be presented to the user. Each one might use different templates.
nlpResponse
The NLP response data for the user message, including the accuracy score, Intent, Entities, and if you have the AL service, the Questions and Documents, the content varies according to what the NLP processed.
userInteractionUUID
String (UUID)
UUID representing the input of the user
User Input
Name
Type
Description
type
String
The type selected by the editor in the Cockpit through the input cell modal.
callToAction
String
For chatbots, text for the input field placeholder for the next message.
pattern
String
When the selected type is ‘Custom’, this field will have the pattern filled by the editor in the Cockpit.
Answer
Name
Type
Description
content
String or JSON Array
Depends on the type of the answer. If it is a Carousel, this field will contain a JSON Array with each card of the carousel.
For a file answer, this field will contain an URL and a filename.
For other types, this content will be String with the content filled by the editor in the Cockpit.
buttons
Button[]
A button list containing all configured buttons for the answer, showing those buttons inside the response card.
quickReply
Button[]
A button list containing all configured quick reply buttons for the answer, showing those buttons as a carousel above the user input.
description
String
The answer’s description. This information may be inserted by the editor in the Cockpit and it serves organizing purposes. It isn't mandatory.
type
String
The card template selected for the answer. Types include:
TEXT_OPTIONS – when the channel is ALL (default response for any channel)
- TEXT - IMAGE - AUDIO - VIDEO - FILE - CAROUSEL - CUSTOM
interactionId
String
UUID representing the current interaction. This value can be used for answers like/dislike (thumbs up and down).
evaluable
Boolean
Will return true if this answer must show a thumbs up / thumbs down (like / dislike) option for the user,
and false otherwise
See Likable service
technicalText
JSON
This is a freeform field, filled by the customer when creating answers in Syntphony CAI's Cockpit. It is recommended that this field is a Json Object, but the client is free to choose which data format to use. If the field is filled as JSON, a JSON object will be returned by the API. This field aims to provide the customer with a resource that complements the experience of its users.
Learn more about all Answer's features in Syntphony CAI
Button
Name
Type
Description
name
String
Text of the button to be shown and sent back as text on the next call, if the button is clicked (depends on the type)
type
String
Possible values:
· URL – if these buttons opens a browser page
· FLOW – if the button is an action in the conversation. In this case, when clicked, other API call must be made using the name of the button as text.
action
String
If the type is URL, this field will have the URL that the browser will open.
Carousel card
Name
Type
Description
imageUrl
String
URL for the image on the card
title
String
Title of the card
subTitle
String
Subtitle of the card
Learn more about Carousel features in Syntphony CAI
NLP Response
Name
Type
Description
type
String
The response's type, whether it is an intent, question or document.
name
String
The name of the response component (intent, question or document) returned by the NLP for the user message.
score
Double
Confidence score for the response component (intent, question or document) above, from 0 to 1.
Entity
Name
Type
Description
name
String
The name of the entity returned by the NLP for the user message.
value
String
The name of the entity value or value entered by the user.
position
A pair of character positions indicating where the entity's value is located within the user's input.
originalValue
String
Original value of the user's text that corresponds to the detected entity
Position
Name
Type
Description
start
Integer
The position of the first character that represents the entity within the user input string.
end
Integer
The position of the last character that represents the entity within the user input string.
Possible Errors
The Conversation API is notable in Syntphony CAI's API's in which it has a long list of possible error codes you'll receive for very detailed response for what went wrong. Like all other Syntphony CAI public API, the error codes and objects can be found at the Integration API page. We encourage you to consult our Broker API's page while implementing so you have an easier time with our response codes.
Sample requests
The request below is an example of a first call to the conversation service, requesting the execution of the welcome flow. It also add a variable to the context, although it is not necessary.
Another possible request, for following user messages:
Another possible request as Intent Navigator (intent/entities are detected previously and prevented from running NLP on Syntphony CAI):
Sample response
The following JSON is an example for a response for the request above.
Loading answers
When you want to avoid NLP calls, Syntphony CAI offers a front-end pre-processing option that bypasses cognitive processing. The CODE practice ties a specific code to a specific answer and obliges Syntphony CAI to deliver this answer.
In Syntphony CAI, a call to the Conversation API with
loads the welcome flow. When this code appears, Syntphony CAI is obliged to load the welcome flow. The extension of this behavior to any other answer is what is called the CODE practice.
When you register an answer name, it will also be its “code”, Syntphony CAI will deliver that specific answer when faced with that code. If the answer is transactional, the transaction is done before the answer is delivered. If the answer is not found, the “code” content is sent to the NLP so it can be interpreted.
When Syntphony CAI API encounters a “code” and a “text”, the code is and the text not (unless the text is used by a transactional component). If an answer with the same name of the “code” content is not found, the “text” content is sent to the NLP. This happens too in the middle of a flow. If a code is sent in the middle of a flow, the flow is stopped to run the code.
So, Syntphony CAI loading priority will be code -> answer -> NLP -> Fallback
Important:
Every code interaction is registered in the User Interactions table
This is useful when you want to build a clickable menu with preset options and each option is a code. For example, a simple menu with options such as “check balance”, “check opening times” and “ask for a refund”.
Learn more about all Answer's features in Syntphony CAI
(WebSocket) Conversation API – STOMP
Overview
This document describes the integration with the EVA Chatbot using WebSocket with the STOMP protocol, enabling real-time bidirectional communication for sending and receiving text messages.
The WebSocket channel mirrors the same:
Business behavior
Session handling
Payload contracts
as the HTTP Conversation API.
Protocol: WebSocket (wss) + STOMP (via SockJS)
Message format: STOMP frames with JSON payload
Audience: General developers
Exposure: Public
The request and response contracts are identical to the HTTP Conversation API
Connection endpoint
Base URL
Both {environment} and {instance} vary per environment.
Example(dev)
Technical note
The broker uses SockJS internally. For Node.js clients, connections should be established using:
Authentication
Authentication happens in two layers:
STOMP CONNECT headers
API Key sent in the SEND frame
CONNECT headers (STOMP)
The following headers are mandatory in the CONNECT frame:
Authorization
JWT token in format Bearer <token>
Organization
Organization UUID
Environment
Environment UUID
Bot
Bot UUID
Channel
Channel UUID
accept-version
Supported STOMP versions (1.2,1.1,1.0)
heart-beat
Heartbeat configuration
Example:
API Key
The API Key must be sent only in the SEND frame, via header:
Session management
JWT tokens expire and can be refreshed using refresh_token.
WebSocket and HTTP share the same session model and business rules, with a clear separation between:
Connection lifecycle (
connectionId)Conversation lifecycle (
sessionCode)
connectionId
Identifies the logical WebSocket connection
Is generated by the client
Is used exclusively in topic and destination URLs
sessionCode
Identifies the conversation session
Is generated and returned by the server
Expires after a period of inactivity
Behaves exactly the same as in the HTTP Conversation API
Rules
The first message must be sent without the
SESSION-CODEheader.After the server returns the
sessionCode, it must be sent as header:
in all subsequent SEND frames.
If the session expires, a new session must be created following the same HTTP rules.
Important: WebSocket and HTTP share the same session model and business rules, with a clear separation between connection lifecycle ( connectionId ) and conversation lifecycle ( sessionCode ).
STOMP Connection flow
After opening the WebSocket, the client must send a CONNECT frame before any other operation.
Subscriptions (SUBSCRIBE)
The client must subscribe to three topics:
Conversation messages
Conversation errors
Conversation events
All path parameters are case-sensitive and must match exactly.
Chat Messages Topic
Error Topic
Events Topic
Sending messages (SEND)
Messages from the user to the chatbot are sent using the SEND frame.
Destination:
SEND Headers
Mandatory headers
API-KEY
API access key
OS
Operating system
LOCALE
Locale (e.g. pt-BR)
USER-REF
User identifier
Conditionally mandatory header
SESSION-CODE
Conversation session identifier
Must NOT be sent in the first SEND
Must be sent in all subsequent SEND frames after the server returns it
Optional headers
OS-VERSION
OS version
BROWSER
Browser name
BROWSER-VERSION
Browser version
BUSINESS-KEY
Business identifier
Origin
Request origin
SEND Payload
The JSON payload uses the exact same contract as the HTTP Conversation API
Example:
All request body fields defined in the HTTP Conversation API apply here.
Receiving messages (MESSAGE)
Responses from the bot are delivered via MESSAGE frames.
The response payload matches the HTTP Conversation API contract.
Example:
Response status
The response status indicates the current state of conversation processing.
Status updates are published as events on the event topic, allowing asynchronous lifecycle tracking.
WAITING_INPUT
The bot finished sending all messages and is waiting for new user input
PROCESSING_MESSAGE
The bot is currently processing the user message
Example response payload:
Context handling
The response status body includes:
context(mutable conversation data)contextReadOnly(read-only server data)
Both are Map<String, Object>.
For each new SEND message, the client must reuse the latest context value received and send it back in the next payload.
Failing to propagate the latest context may result in inconsistent behavior or loss of state.
Error handling
Errors are delivered asynchronously through the error topic.
They do not automatically close the WebSocket connection.
Example:
Error codes follow the same pattern as the Conversation API error model
Business rules
WebSocket integration shares the same business logic as HTTP API
Request and response contracts are identical
Clients must consume messages until FINISHED
Appendix — Diagram, JavaScript Example (Node.js) – SockJS + STOMP
Sequence diagram
JavaScript Example (Node.js) – SockJS +
STOMP
How to Run (Node.js)
Prerequisites
Node.js 16+
Internet access to EVA endpoints
Check Node version:
Create a project
Install dependencies
Enable ES Modules Edit
package.jsonand add:
Create the Script
Create index.js and paste the JavaScript example above.
Fill all required input variables at the top of the file.
Run
Expected output
Successful STOMP connection logs
Chat messages printed to console
Errors (if any) printed from error topic
Final message with status = FINISHED
(Audio) Conversation API
Method
POST
URL:
/org/{orgUUID}/env/{envUUID}/bot/{botUUID}/channel/{channelUUID}/v1/conversations/ or /org/{orgUUID}/env/{envUUID}/bot/{botUUID}/channel/{channelUUID}/v1/conversations/{sessionCode}
Type:
multipart/form-data
As mentioned before, your implementation of the Conversation API for audio or text input remains uses the same endpoint and is interchangeable. Syntphony CAI distinguishes them according to the content-type submitted.
When your submitted content-type is a multipart/form-data structure, Syntphony CAI will discern this implies you are sending an audio file. At this point, the behaviour of the API remains mostly the same - the response, expected headers and parameter structure will not change.
The only part that differs from the text input Conversation API is the Body, as seen below:
Request body (Audio only)
Name
Type
Required
Description
file
FILE
Yes
The audio file. It's specifications are detailed below.
conversationRequestJson
JSON
Yes
The exact body of the textual conversational API. Notably relevant because the Context field holds your open, visible and hidden context variables and they must be supplied for continuity. Submitted 'text' or 'code' fields will not trigger errors, but will be ignored.
Audio File Specifications
The supplied audio file must comply with some standards in order to be accepted.
The audio file must be no larger than 16 Mb, and it's file type must be one of the following:
ogg
wav
Another restriction is it's time limit. Any supplied audio file must be no longer than one minute in lenght. While this will not trigger any API error, any content past the first minute will be ignored.
Likable Service
Method
POST
URL:
/org/{orgUUID}/env/{envUUID}/likable
Type:
application/json
The likable service is used when an answer is configured to be evaluable. When this option is enable, the answer should give the user a thumps up / thumbs down option (like / dislike) in the chat.
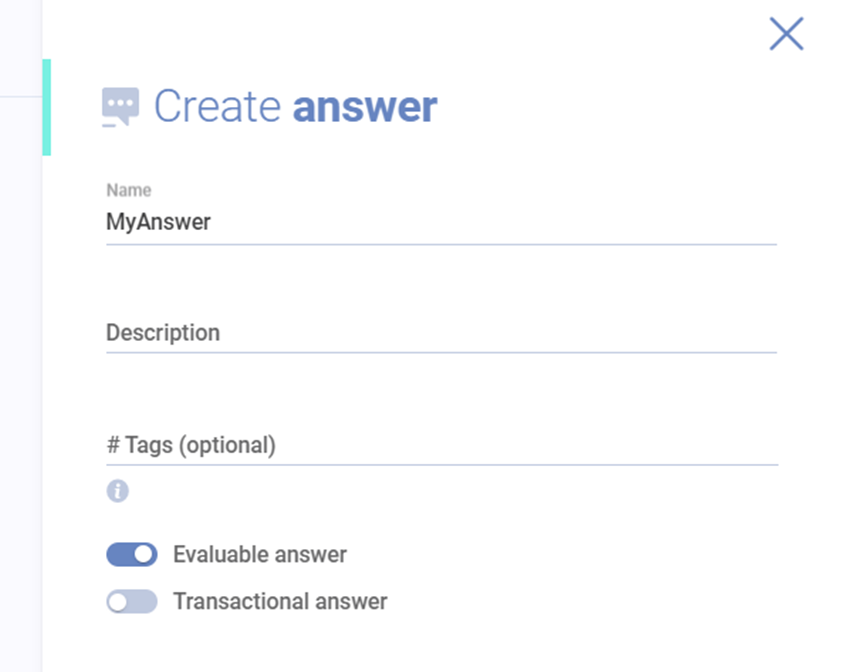
When the user likes or dislikes an answer, this service must be called.
URL parameters
Name
Type
Required
Description
orgUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of your organization. Your token is verified over this field.
envUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of the environment your bot is located. Your token is verified over this field.
Request headers
Name
Type
Required
Description
API-KEY
String
Yes
Api key for client identification. The environment administrator must provide this data.
Request body
Name
Type
Required
Description
evaluation
Boolean
Yes
True, if user liked the answer (thumbs up), and false, if user disliked the answer (thumbs down)
interactionId
String
Yes
The answer's interactionId, acquired in the conversation service response Answer object.
Response body
The likable service will return a HTTP Status 200 with a “Success” string.
Sample request
Sample Response
"Success"
Satisfaction service
URL:
/conversations/{sessionCode}/satisfactions
Type:
application/json
When the conversation ends, a form might be given to the user to evaluate the virtual agent. This evaluation has 3 parts:
A yes/no question asking the user if his doubt or if the problem was solved.
A grade for the conversation. The range can vary, but it is recommended to use a 0 to 10 grade.
Comments field for any details the user might want to add.
Important:
This service can be called only once for each sessionCode
URL parameters
Name
Type
Required
Description
orgUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of your organization. Your token is verified over this field.
envUUID
String
Yes
The UUID of the environment your bot is located. Your token is verified over this field.
Request headers
Name
Type
Required
Description
API-KEY
String
Yes
API key for client identification. The environment administrator must provide this data.
LOCAL
String
Yes
Virtual agent’s language: <language>-<COUNTRY>
This must be the same as configured in the Cockpit.
Examples:
- en-US - es-ES - pt-BR
Request body
Name
Type
Required
Description
evaluation
Short number
Yes
This number represents how the user graded the virtual agent. It is recommended to be a number from 1 to 10, but can be changed to use other systems (i.e. 5 stars)
answered
Short number
Yes
Considering that a user interacts with a virtual agent to have a question/problem answered:
1 – the user had its problem solved
0 – his problem was not solved
userComments
String
No
User comments about the session.
expireSession
Boolean
Yes
·This value must be true if you wish the session to immediately be expired when the user sends this evaluation.
It should be false instead if the session must not be expired so that the conversation might still continue
Response body
The satisfaction service will return a HTTP Status 200 with a “Success” string.
Sample request
Sample response
"Success"
Recommended Practices
Message Protection
Messages sent to the conversation API are sent with both the user’s message data, which may contain sensitive information and with your Syntphony CAI token.
While one attempt a straightforward implementation in their front-end website that immediately calls our API, we highly recommend against that as it can endanger your user's data, your token integrity, and breaches the GDPR.
Leaving this valuable information exposed may be exploited and also exposes your token to anyone who wants it in the console. Furthermore, your data is now spoofable by softwares such as sharks which may intercept your messages if they are transmitted with their data in a human language.
Sending your raw requests from the front-end is an understandable practice during your development phase, but we highly recommend you to add a custom security layer for this data, encrypting all messages sent by the front-end.
One adequate way to do this, is to have your back-end act as a security intermediate. A secure message flow would have the messages your user is sending though your chat, encrypted by a library such as CryptoJS, sent to your back-end server instead, which will then decrypt the message and send the request to the Conversation API itself, where the data is not spoofable or exploitable by users.
Last updated
Was this helpful?